Ever notice those ads that appear right at the top of your search results? Or wonder how companies seem to know exactly when you’re interested in their products? That’s the magic of pay-per-click advertising, and if you’ve been curious about how it all works, you’ve landed in the right place. Welcome to “PPC 101” – your friendly guide to understanding the world of pay-per-click advertising.
In this comprehensive post, we’ll explore everything from the fundamental concepts of PPC to practical strategies you can implement right away. Whether you’re a small business owner looking to expand your reach or a marketer wanting to sharpen your digital skills, this guide will walk you through the essentials without the confusing jargon.
By the time you finish reading, you’ll have the knowledge to launch your own PPC campaign with confidence. We’ll cover keyword research, creating compelling ad copy, optimizing landing pages, and much more. Plus, you’ll discover how to set realistic budgets and avoid costly mistakes that trip up many beginners. Let’s dive in!
Introduction to PPC 101
Pay-Per-Click (PPC) is exactly what it sounds like – an advertising model where you only pay when someone clicks on your ad.
What Is Pay-Per-Click (PPC)?
In its simplest form, PPC is a digital advertising approach designed to drive immediate traffic to your website. Unlike other marketing methods that can take months to show results, PPC can deliver traffic as soon as your ads are approved and running. It’s like turning on a tap of potential customers whenever you need them.
Why PPC Matters for Businesses
PPC advertising gives businesses of all sizes the power to appear in front of potential customers exactly when they’re searching for related products or services. Whether you run a local coffee shop or a multinational corporation, PPC helps level the playing field and allows you to compete for valuable traffic regardless of your company size.
Overview of This Ultimate Guide to Pay-Per-Click Advertising
In the following sections, we’ll explore everything from the fundamentals to advanced strategies like remarketing and conversion optimization. We’ll demystify essential terms like cost-per-click (CPC) and click-through rate (CTR), so you can speak the language of digital advertising with confidence. By the end, you’ll have a solid foundation for creating and managing your own PPC campaigns across various platforms.
Understanding the Basics
What Are PPC Ads?
PPC ads take many forms, but the most recognizable are those search ads that appear at the top of Google’s results pages. These listings are marked as “sponsored” or “ad,” and advertisers pay a fee only when someone clicks on them. According to Google’s Economic Impact Report, businesses make an average of $2 in revenue for every $1 they spend on Google Ads.
How Does Pay Per Click Work?
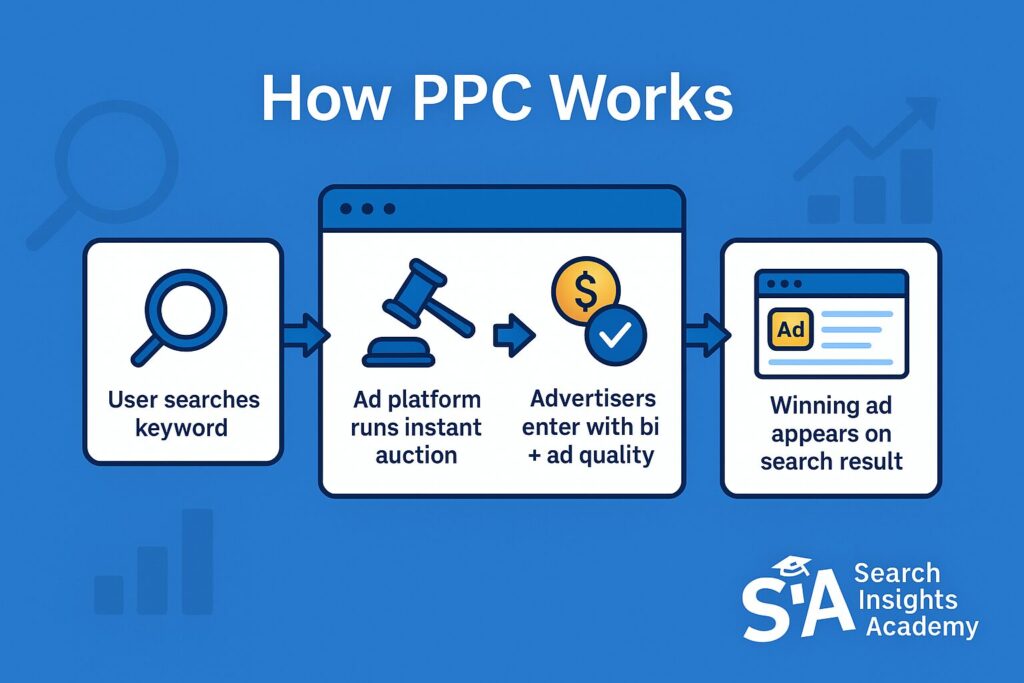
The process works through an auction system. You select keywords relevant to your business and set bids on how much you’re willing to pay when someone clicks your ad after searching for those terms. When a user searches for that keyword, an instant auction determines which ads appear and in what order.
PPC vs. Organic Search: Key Differences

Organic search results are “free” in that you don’t pay per click, but they require significant investment in search engine optimization (SEO) and can take months to show results. PPC ads provide immediate visibility but come with a direct cost. Many successful digital marketing strategies leverage both approaches for maximum impact.
Ad Auctions and How Bidding Works
Google Ads and other platforms run auctions that consider not just your maximum bid but also the quality and relevance of your ad. This system, called Ad Rank, takes into account your bid amount, ad quality, and the expected impact of extensions and other ad formats.
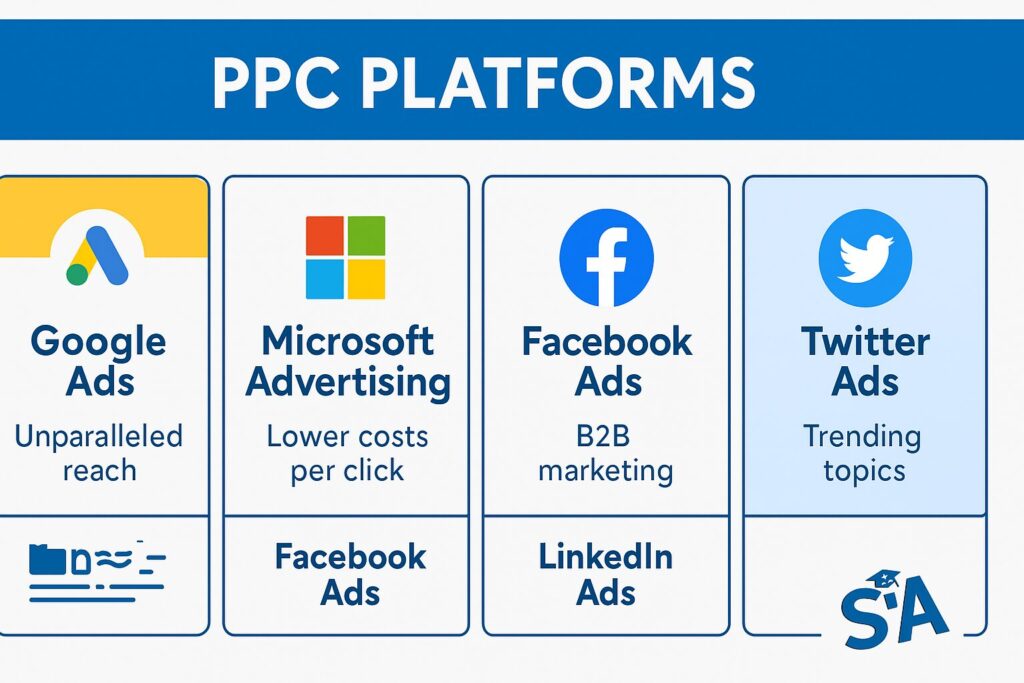
Overview of Common PPC Platforms
While Google Ads dominates the market with over 92% of search engine market share, Microsoft Advertising (formerly Bing Ads) offers access to the Yahoo! and Bing networks, reaching millions of users Google doesn’t. Other platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn offer their own versions of PPC advertising with unique targeting capabilities.
Key Terms: CPC, CTR, and Quality Score
- Cost Per Click (CPC): The amount you pay each time someone clicks your ad
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): The percentage of people who click your ad after seeing it
- Quality Score: Google’s rating of the quality and relevance of your keywords and PPC ads
What Is the Difference Between PPC and Traditional Advertising?
Traditional advertising typically requires upfront payment regardless of performance. Whether anyone sees your billboard or newspaper ad, you pay the same amount. With PPC, you only pay when someone actively engages with your ad, making it easier to track return on investment and adjust campaigns in real-time.
Choosing the Right PPC Platform
PPC Advertising Google Ads: An Introduction
Google Ads (formerly AdWords) is the world’s largest and most popular PPC advertising platform. With access to billions of daily searches, it helps businesses connect with potential customers at the exact moment they’re looking for related products or services. Google processes over 8.5 billion searches per day, giving advertisers unprecedented reach.
Google Ads: Key Features and Benefits
Google Ads offers flexible budgeting (start with as little as $5 per day), powerful targeting options, and various ad formats including:
- Search ads (text-based ads on search results pages)
- Display ads (visual ads across websites in the Google Display Network)
- Video ads (on YouTube and partner sites)
- Shopping ads (product listings with images and prices)
The platform also provides robust analytics and reporting tools to help you understand what’s working and optimize accordingly.
Exploring Other Platforms
While Google Ads dominates the market, other platforms offer unique advantages:
- Microsoft Advertising: Reaches the Bing, Yahoo, and DuckDuckGo search networks with typically lower costs per click and less competition
- Facebook Ads: Allows targeting based on interests, behaviors, and detailed demographics rather than search intent
- LinkedIn Ads: Particularly effective for B2B marketing with targeting options based on job title, company size, and industry
- Twitter Ads: Good for joining conversations around trending topics and events
People Also Ask: “Is Google Ads the Only Option for PPC?”
Absolutely not. While Google Ads is the largest platform, many businesses find success with a multi-platform approach. Depending on your audience and objectives, platforms like Pinterest, Snapchat, or even TikTok might deliver better results for specific campaigns.
Planning Your PPC Campaign
Step-by-Step Tutorial for Beginners
Starting your first PPC campaign doesn’t have to be overwhelming. Here’s a simplified approach:
- Define clear objectives – Whether it’s generating leads, driving sales, or building awareness
- Choose your platform – Most beginners start with Google Ads due to its reach and user-friendly interface
- Identify your target keywords – Use tools like Google Keyword Planner to find relevant search terms
- Set your budget – Determine how much you’re willing to spend daily or monthly
- Create your first ad group – Bundle related keywords and write compelling ad copy
- Launch and monitor – Start your campaign and closely track performance
Targeting the Right Audience
Effective PPC campaigns reach the right people at the right time. Modern platforms offer sophisticated targeting options including:
- Geographic targeting – From countries down to specific postal codes
- Demographic targeting – Age, gender, income level, and parental status
- Device targeting – Desktop, mobile, or tablet users
- Time targeting – Show ads only during specific hours or days
Research shows that targeted advertising can increase conversion rates by up to 300%, making it crucial to refine your audience parameters.
Budgeting and Bidding Strategies
You can manage your PPC budget through various bidding strategies:
- Manual CPC – You set the maximum amount you’re willing to pay per click
- Automated bidding – The platform adjusts your bids based on your goals
- Enhanced CPC – A hybrid approach where you set manual bids but allow the system to adjust them
According to a study by WordStream, the average cost per click across all industries is $2.69 for search and $0.63 for display, but this varies widely by sector.
People Also Ask: “What Is Pay Per Click Marketing?”
Pay Per Click marketing is the practice of using paid advertising where you pay each time someone clicks on your ad. It encompasses everything from keyword research and ad creation to bid management and performance analysis. Unlike organic marketing methods, PPC delivers traffic immediately but requires ongoing investment.
Keyword Research and Strategy
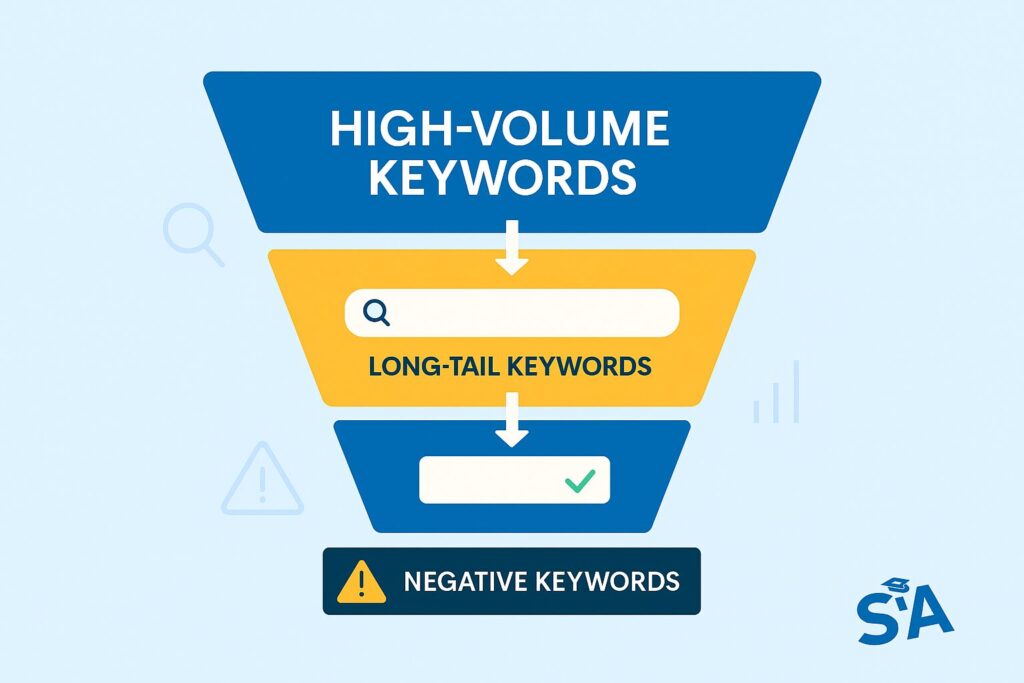
Identifying Low-Hanging Fruit Keywords
Successful PPC campaigns start with effective keyword research. Begin by identifying terms that balance search volume with competition:
- Brainstorm terms related to your products or services
- Use keyword research tools like Google Keyword Planner or SEMrush to expand your list
- Look for “low-hanging fruit” – keywords with decent search volume but lower competition
- Consider long-tail keywords (longer, more specific phrases) that typically have lower costs and higher conversion rates
Using High-Volume Keywords Effectively
While high-volume keywords can drive substantial traffic, they often come with intense competition and higher costs. To use them effectively:
- Balance them with more specific, lower-competition terms
- Improve your Quality Score to reduce costs (through relevant ad copy and landing pages)
- Use match types strategically to control when your ads appear
- Monitor performance closely and adjust bids based on conversion data
Negative Keywords: Why They’re Crucial
Negative keywords prevent your ads from showing for irrelevant searches, helping you:
- Reduce wasted spend on non-converting clicks
- Improve your click-through rate and Quality Score
- Focus your budget on searches with genuine buying intent
Research by WordStream found that adding negative keywords can reduce wasted ad spend by up to 30%, making this an essential optimization strategy.
People Also Ask: “Which Keywords Should I Choose for a Successful PPC Campaign?”
The most effective keywords for your campaign should:
- Match user intent (what people are actually looking for)
- Be relevant to your business and offerings
- Have sufficient search volume to generate traffic
- Fit within your budget constraints
- Show clear commercial intent if your goal is conversions
Studies show that matching keywords to the buyer’s journey stage can significantly improve campaign performance.
Writing Compelling Ad Copy

Crafting Headlines and Descriptions That Convert
Your ad copy is often the first impression potential customers have of your business. To create compelling PPC ads:
- Include your primary keyword in the headline for relevance
- Highlight unique selling points (what makes you different)
- Address customer pain points or desires
- Use numbers and specific claims when possible (e.g., “50% Off” or “Save $100”)
- Create a sense of urgency (“Limited Time” or “While Supplies Last”)
- End with a clear call-to-action that tells people exactly what to do next
According to Unbounce, ads with a strong call-to-action can increase clicks by up to 90%.

Quality Score and How to Improve It
Quality Score is Google’s rating of the quality and relevance of your keywords and PPC ads. Higher scores can lead to lower costs and better ad positions. To improve your Quality Score:
- Ensure tight thematic organization of ad groups (related keywords grouped together)
- Write highly relevant ad copy that includes your keywords
- Create landing pages that deliver on your ad’s promise
- Improve your click-through rate with compelling offers
- Add negative keywords to prevent irrelevant impressions
Google has confirmed that a high Quality Score can reduce your cost per click by up to 50%.
People Also Ask: “What Is the Best Way to Increase CTR?”
To improve your click-through rate:
- Write attention-grabbing headlines that address user needs
- Test different value propositions to see which resonates best
- Include prices, promotions, or exclusivity when relevant
- Use ad extensions to provide additional information and increase ad real estate
- Implement countdown timers for limited-time offers
Research by Wordstream found that the top 25% of Google Ads accounts have an average CTR of 6.05% or higher in the search network.
Landing Pages and Conversion Optimization
Designing Effective Landing Pages
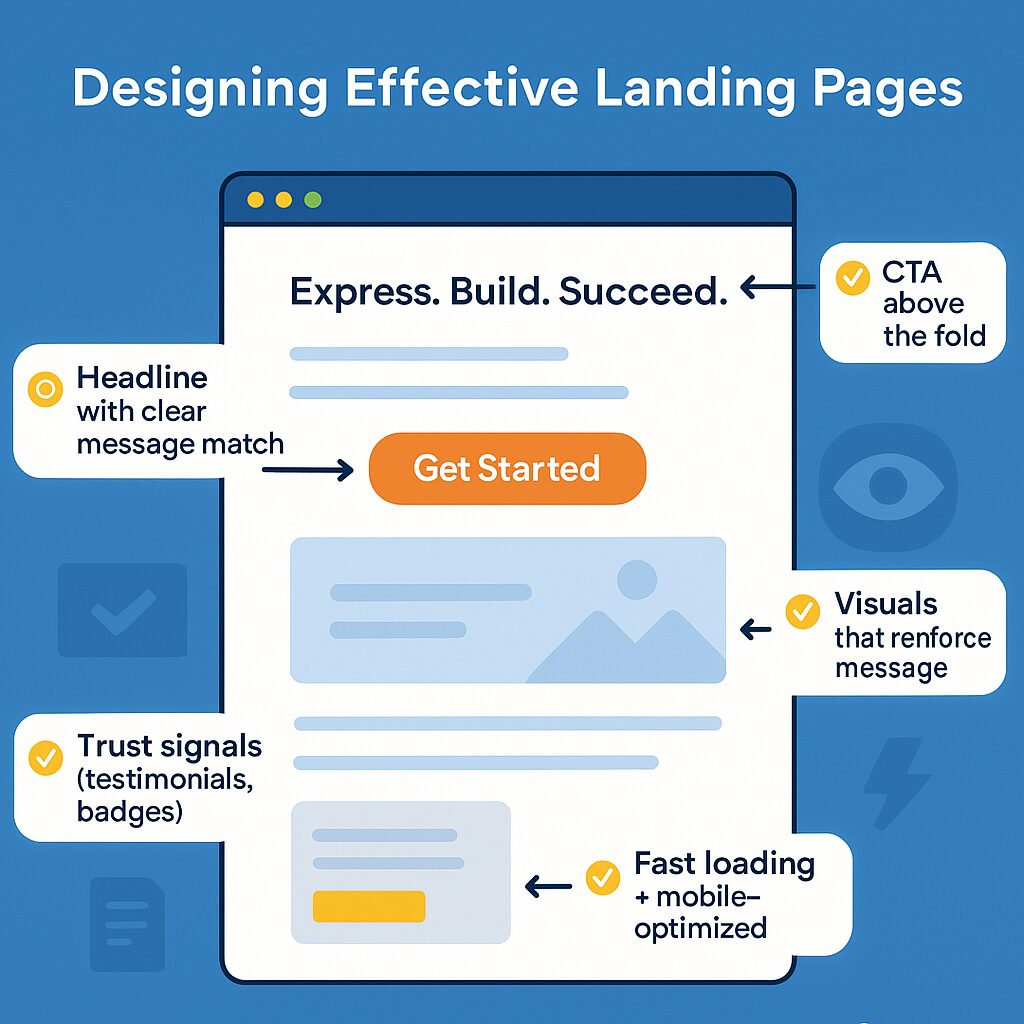
Your landing page is where the conversion happens – it needs to deliver on the promise of your ad and guide visitors toward taking action. For effective landing pages:
- Maintain message match between your ad and landing page
- Keep the design clean and focused on a single conversion goal
- Place your main call-to-action above the fold (visible without scrolling)
- Use compelling visuals that support your message
- Include trust signals like testimonials, reviews, or security badges
- Optimize page load speed (each second of delay reduces conversions by 7%)
- Make your forms as simple as possible (fewer fields = higher conversion rates)
Tracking Conversions and Measuring ROI
Without proper tracking, you’re flying blind. Set up conversion tracking to understand which ads, keywords, and audience segments deliver results:
- Install Google Analytics and connect it to your Google Ads account
- Define conversion actions (purchases, form submissions, calls, etc.)
- Assign values to conversions to calculate return on investment
- Use UTM parameters to track traffic from different campaigns
- Set up regular reporting to monitor performance
With proper tracking, you can calculate your actual return on ad spend (ROAS) and make data-driven decisions about where to allocate your budget.
People Also Ask: “How Do I Turn PPC Clicks into Conversions?”
The key to converting PPC traffic lies in alignment and optimization:
- Ensure your landing page fulfills the specific promise made in your ad
- Test different headlines, images, and call-to-action buttons
- Implement A/B testing to continuously improve conversion rates
- Address potential objections directly on your landing page
- Use heat mapping tools to understand how visitors interact with your page
According to CXL Institute, companies that invest in conversion rate optimization see an average ROI of 223%.
Campaign Management and Ongoing Optimization
PPC Management Tools and Best Practices
Managing PPC campaigns efficiently requires the right tools and processes:
- Google Ads Editor: A free desktop application for bulk campaign management
- Third-party tools: Platforms like SEMrush, Ahrefs, or Optmyzr offer advanced management capabilities
- Automated rules: Set up conditions to automatically pause underperforming ads or adjust bids
- Scripts: Use Google Ads scripts to automate repetitive tasks and analysis
- Scheduling: Review and optimize campaigns on a consistent schedule
Best practices include regular account audits, testing new ad variations, and staying updated on platform changes and new features.
Monitoring Key Metrics: CPC, CPA, and ROAS

Focus on these critical metrics to evaluate performance:
- Cost Per Click (CPC): How much you’re paying for each click
- Cost Per Acquisition (CPA): The total cost to acquire a customer or conversion
- Return On Ad Spend (ROAS): Revenue generated for every dollar spent on advertising
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of clicks that result in conversions
- Quality Score: Google’s rating of your keyword and ad relevance
According to a study by Databox, 78% of PPC experts consider ROAS the most important metric for evaluating campaign success.
People Also Ask: “How Often Should I Review My PPC Ads?”
For new campaigns, daily monitoring is advisable during the first few weeks. Once performance stabilizes, weekly reviews are typically sufficient for most businesses. However, for accounts with large budgets or during peak seasons, more frequent checks may be necessary.
Common PPC Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them

Overspending on Irrelevant Clicks
One of the fastest ways to waste your PPC budget is paying for clicks that have no chance of converting. Prevent this by:
- Implementing a comprehensive negative keyword strategy
- Using appropriate match types (exact, phrase, or broad match modified)
- Regularly reviewing search term reports to identify irrelevant queries
- Setting up IP exclusions for competitors or bot traffic
- Creating tightly themed ad groups with focused keyword sets
Failing to Test Ad Variations
Running a single ad version limits your ability to improve performance. Instead:
- Create at least 2-3 variations for each ad group
- Test different headlines, descriptions, and calls-to-action
- Use Google’s built-in ad rotation and optimization features
- Allow sufficient data collection before drawing conclusions
- Apply learnings from successful ads across your account
Neglecting Mobile Searches
With over 60% of searches now coming from mobile devices, overlooking mobile optimization is a costly mistake:
- Create separate bid adjustments for mobile devices
- Design mobile-friendly landing pages with fast load times
- Use call extensions to make it easy for mobile users to contact you
- Consider the mobile user experience in your ad copy and offers
- Review performance metrics separately for mobile and desktop
People Also Ask: “Why Isn’t My PPC Campaign Performing?”
Common reasons for underperforming campaigns include:
- Insufficient budget for your competitive landscape
- Poor keyword selection or match type settings
- Low Quality Scores leading to higher costs and lower positions
- Disconnects between ad copy and landing pages
- Targeting too broad an audience
A detailed audit using Google’s PPC audit template can help identify specific areas for improvement.
Scaling and Expanding Your PPC Efforts
Exploring New Markets and Platforms
Once you’ve established a successful PPC foundation, consider expansion:
- Test new geographic regions where your products or services might resonate
- Experiment with additional platforms that reach different audience segments
- Adapt your messaging for different markets and cultures
- Allocate small test budgets before making major investments
- Use Google’s Market Finder tool to identify promising international markets
Remarketing Campaigns: Tips and Tricks
Remarketing (also called retargeting) allows you to reconnect with people who’ve previously visited your site:
- Create segmented lists based on specific pages visited or actions taken
- Develop tailored messaging that acknowledges previous interactions
- Set appropriate frequency caps to avoid ad fatigue
- Use dynamic remarketing to show specific products viewed
- Implement sequential messaging that guides users through the funnel
According to Google’s own research, remarketing campaigns can boost conversion rates by up to 150%.
People Also Ask: “How Do I Scale My PPC Without Overspending?”
Scaling PPC effectively requires a methodical approach:
- Increase budgets incrementally (10-20% at a time) while monitoring performance
- Expand to related keywords that show similar conversion patterns
- Test new audience segments based on your best-performing demographics
- Add additional ad formats (display, video, shopping) to existing campaigns
- Maintain or improve ROAS as you scale by continuously optimizing
A study by Disruptive Advertising found that gradual scaling with consistent performance monitoring delivers the best long-term results.
Conclusion and Further Resources

Recap of Key Takeaways for PPC 101
We’ve covered the essential building blocks of successful PPC advertising:
- Understanding the fundamentals of how pay-per-click works
- Selecting the right platforms for your business objectives
- Conducting thorough keyword research and implementing effective bidding strategies
- Creating compelling ad copy that drives clicks
- Designing landing pages that convert visitors into customers
- Managing campaigns efficiently and optimizing for better performance
- Avoiding common pitfalls that waste budget
- Scaling campaigns strategically as you grow
Remember that successful PPC is an ongoing process of testing, learning, and refining based on data.
Next Steps and Additional Resources
To continue developing your PPC skills:
- Follow industry blogs like Search Engine Journal, PPC Hero, and the Google Ads Blog
- Take free courses like Google’s Skillshop certifications
- Join PPC communities on Reddit, Facebook, or LinkedIn to learn from peers
- Consider using tools like SEMrush or Ahrefs to enhance your keyword research
- Set up regular A/B tests to continuously improve performance
The most important step is to start implementing these strategies in your own campaigns, measuring the results, and adapting based on what you learn.
The digital advertising landscape continues to evolve, but the core principles of effective PPC remain: reach the right people, with the right message, at the right time – and only pay when they click. With the foundation you’ve gained from this guide, you’re well-equipped to launch and grow successful PPC campaigns that drive measurable results for your business.

