Ever wonder how Google or Bing manage to sift through billions of websites in seconds and present you with the exact information you need? Have you noticed how certain pages always seem to rank higher than others? And why do some sites get fresh content displayed within hours, while others take days or weeks to appear in search results?
This post aims to answer those questions by taking you on a friendly journey through the core processes that make search engines tick. We’ll talk about how these platforms explore the web (crawling), organize massive amounts of data (indexing), and arrange search results in the order you see on your screen (ranking). On top of that, we’ll explore the vital role of keyword research. You’ll learn about low hanging fruit keywords, how to conduct initial keyword research, and why competitive phrases sometimes require more effort.
You can look forward to clear explanations, real-world examples, and handy tips for boosting your site’s visibility. We’ll discuss best practices that ensure your content, whether it’s a local service page or a global e-commerce platform, finds its way onto the search engine radar. By the end, you’ll understand how search engines work at a fundamental level and how to perform effective keyword research for maximum impact. Let’s dive into these fundamentals, so you can harness the power of search technology and position yourself ahead in this online era.
Why Understanding Search Engines Matters
To thrive online, it is vital to know how search engines function. Whenever you make a query—like “best running shoes” or “Italian restaurants near me”—the search engine’s main job is to deliver the most relevant content in a lightning-fast manner. If your site is not aligned with how these platforms organize information, you could be missing out on valuable visitors.
On top of that, search engine optimization (SEO) isn’t just about gaining a higher spot; it’s about meeting user needs. When you appear in the top positions, potential customers are more likely to trust you. According to a study by Advanced Web Ranking, the first position on Google search results has an average click-through rate of 27.6%. By truly understanding search engine behavior, you can tailor your content strategy, build stronger authority, and stand out in your industry, regardless of where your business is located.
Key Terminologies in SEO (Keywords, Crawling, Indexing, Ranking)
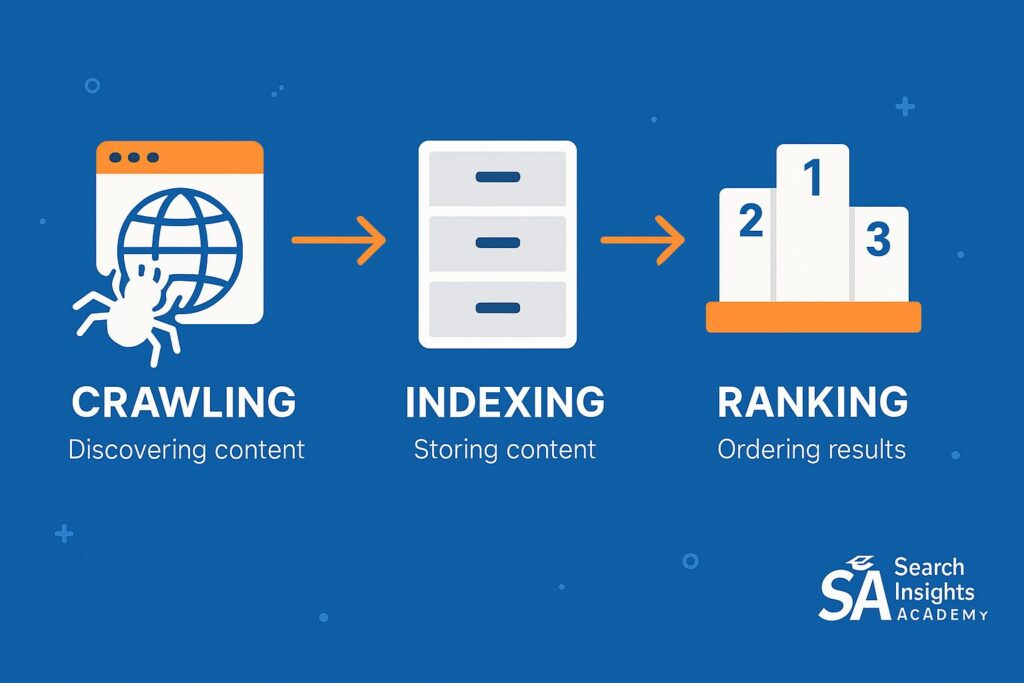
Before we explore each stage, let’s briefly define these essential terms. “Crawling” is how a search engine scours the web, visiting site after site and collecting data. According to Google, their crawlers follow links from one page to another, building a map of the web as they go.
“Indexing” revolves around organizing that data and storing it, so it can be retrieved in a split second whenever someone searches. “Ranking” then arranges web pages based on relevance and authority, pushing the best matches higher up the list. Finally, “keywords” are the words or phrases people type into search bars. These terms connect user intent with the most appropriate content. Knowing these definitions sets the foundation for understanding how your website will be discovered and displayed on search engines.
The Fundamentals of How Search Engines Work
The process might feel like magic, especially when results appear in the blink of an eye. But at the heart of it, search engines utilize complex algorithms to evaluate millions of data points. These algorithms identify content relevance, check site authority, and match user queries to the best content possible. If your content matches user intent, you stand a higher chance of snagging those impressive top rankings.
Search engines don’t rely on a single factor. Instead, they look at your site’s performance (page speed, mobile-friendliness), content quality (original, helpful), and inbound links (reputable sites linking back to you). When done well, these aspects elevate your site’s trustworthiness. Although we often discuss Google because it holds a dominant global market share of over 90%, Bing, Yahoo, Baidu, and other search engines follow similar patterns.
It’s essential to note that algorithms evolve continuously. Google makes thousands of algorithm updates each year, with some major updates dramatically shifting the SEO landscape. Techniques that worked well in 2017 might not cut it for 2023 or beyond. By staying on top of these shifts, you can remain competitive and keep driving traffic. Now, let’s take a closer look at the three core pillars of search engine operation—crawling, indexing, and ranking—and see why they matter to your overall SEO strategy.
Overview of Search Algorithms
Search algorithms are like the secret sauce that determines which web pages best satisfy a given query. They’re designed to interpret the user’s intent behind a phrase rather than just looking at the words themselves. According to Search Engine Journal, Google’s algorithms have evolved from simple keyword matching to complex systems that understand semantics and context.
These algorithms evolve with machine learning and advanced data analysis. As a site owner or content creator, your goal is to align your site with these evolving algorithms. By focusing on high-quality content, user experience, and relevant keywords, you help search engines recognize your value and showcase your pages to the right audience.
The Importance of Relevance and Authority
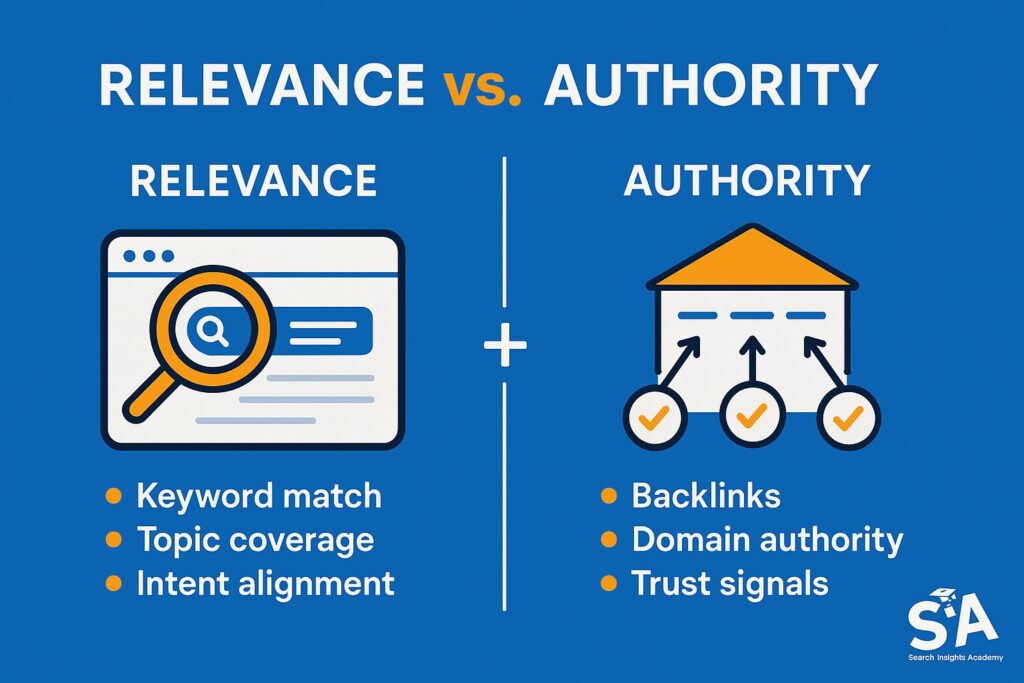
Relevance is all about matching the user’s query to your page content. If someone types “how to train for a marathon,” your page should provide answers on exactly that topic. Authority, on the other hand, is tied to how credible or trustworthy your site is. Moz’s Domain Authority is one popular metric that attempts to measure this concept, with backlinks from recognized sources being a key factor.
In the eyes of search engines, relevance alone isn’t enough if your site lacks authority. The best approach is to combine the two. Make sure that your content is laser-focused on targeted keywords, and support it with a strong network of backlinks. Achieving that balance gives your site an edge in the online realm.
Crawling: Exploring the Web
“Crawling” is the stage where search engines dispatch bots, often called “spiders,” to roam across websites. These bots follow links from one page to the next, gleaning essential data about each page’s content and structure. When businesses create new web pages or edit old ones, these changes matter only if the bots actually crawl and spot them.
Sometimes, though, these bots face challenges. For example, site owners may unintentionally block them through incorrect settings or complicated site structures. A study by Botify found that search engines typically crawl less than 60% of most websites’ pages. This can result in pages never being crawled at all, which means they won’t be indexed and, in turn, won’t appear in search results. Keeping track of how your site is navigated can address such problems early on.
Crawling frequency is another hot topic. A common question is “How often do search engines crawl websites?” Though it varies by site authority and update frequency, Google re-crawls popular pages more often. Meanwhile, smaller or lesser-known sites might see fewer crawl visits. Building a tidy site with a clear URL structure and fresh content can encourage more frequent crawls, giving your brand a better chance of staying current in the eyes of search engines.
What Is Crawling and Why Does It Matter?
Crawling is how search engines collect data about your site. These automated programs gather page details, meta tags, and link structures, then add that information to their master database. Google’s own documentation explains that Googlebot is their primary web crawler that discovers pages by following links.
This matters because if a bot never discovers a page, it cannot appear in search results for any search queries. Proper crawling ensures that every important page of your site is documented, giving you a chance to reach people hunting for phrases directly related to your products or services.
How Often Do Search Engines Crawl Websites? (People Also Ask)
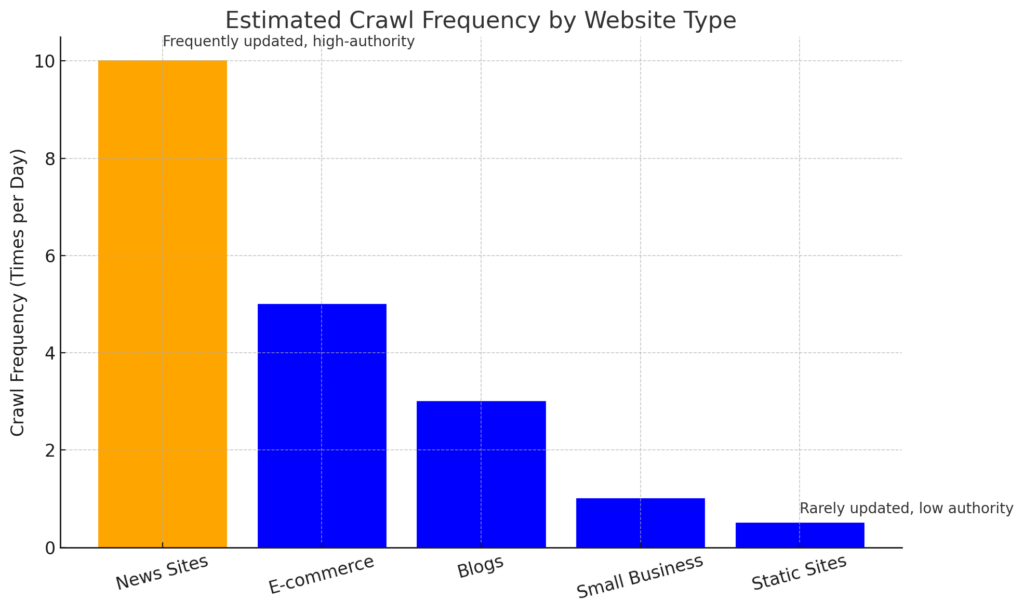
Search engines typically prioritize sites that publish fresh or popular content. Large, frequently updated websites, like news outlets, might be crawled multiple times a day. Smaller or static sites could be visited every few weeks. Optimizing your site structure and regularly publishing quality content can boost crawling frequency.
Common Crawling Challenges for Websites
Common obstacles include broken links, slow page load times, or accidental blocking of search bots via your robots.txt file. According to DeepCrawl, improper robots.txt configuration is one of the most common technical SEO issues. These technical slip-ups can be costly, reducing your site’s visibility in the long run.
To avoid these challenges, routinely audit your site for crawl errors in platforms like Google Search Console. This ensures your valuable content is easily discovered by search engine spiders.
Indexing: Organising the Internet
After a bot crawls a page, it stores details about that page in an immense digital library known as the “index.” Indexing involves taking note of page titles, meta descriptions, topics, and any relevant links. Think of it like librarians cataloguing books, so it’s easier to find what you need later.
One of the most common questions is “What is the Google index?” In simple terms, it’s Google’s record of all the pages it’s crawled and deemed valuable enough to show in search results. According to Google’s own explanation, they store information in the Google index, a database that’s over 100,000,000 gigabytes in size. If your page doesn’t make it into this index, it’s practically invisible. People searching terms like “best chocolate chip cookie recipe” will never see it, even if your page addresses that aspect perfectly.
Making sure your pages get indexed involves having clear sitemaps, relevant internal links, and no major technical errors. A study by Ahrefs found that a significant percentage of pages never get indexed due to quality issues or crawl problems. Over time, you’ll want to keep an eye on which pages are indexed and which aren’t. That way, you can address any indexing failures before they cost you valuable traffic and potential customers.
How Search Engines Store and Organise Data
Search engines transform the collected data into a structured format, allowing quick retrieval. Pages are classified by topic, popularity, and even user behavior history. According to Stanford University’s explanation of search engines, this organization is crucial for efficiently processing billions of queries daily.
This careful organization helps users get relevant results fast—typing in “how to fix a leaky faucet,” for instance, triggers the engine to sift through its optimized database for the most accurate answers. Without indexing, it would take far too long to pinpoint the pages that match a user’s request.
What Is the Google Index? (People Also Ask)
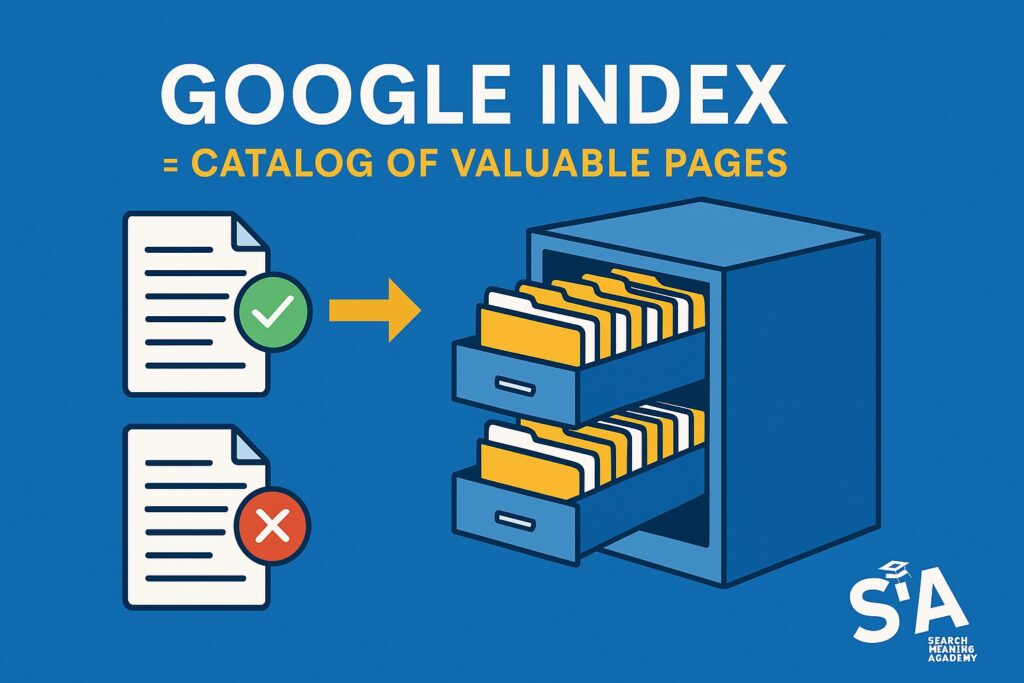
Simply put, the Google index is the comprehensive library of web pages that Google’s bots have crawled and deemed suitable to present to users. Search Engine Journal explains that unindexed pages remain hidden from public view, regardless of their quality or relevance.
Ensuring Your Content Is Properly Indexed
For proper indexing, use a well-structured sitemap, monitor your Search Console for errors, and avoid duplicate content. Moz’s guide to XML sitemaps explains that these files help search engines understand your site structure. Make sure that your site’s most valuable pages aren’t blocked by robots.txt. Keeping XML sitemaps updated ensures search engines are aware of new content, helping it appear quickly for relevant searches.
Ranking: Positioning in the Search Results
Ranking is all about deciding which pages deserve the prime real estate at the top of the search results. Numerous factors come into play here. The quality of your content and the presence of essential keywords serve as the starting point. High-ranking pages address the searcher’s question immediately and are considered trustworthy. Backlinko’s analysis of ranking factors found that comprehensive content that thoroughly answers user queries tends to rank higher.
Search engines also measure user engagement. That’s where metrics like click-through rate, time on page, and bounce rate become vital. If users consistently find your page helpful—say they stick around and read thoroughly—search engines may boost its ranking further. On the flip side, if visitors bounce quickly, the algorithms assume your page may not be relevant.
Another element influencing where you appear is user experience (UX). If a user has to scroll endlessly or is bombarded with intrusive ads, they’ll likely leave. Google’s Page Experience Update explicitly made UX factors ranking signals. This dissatisfaction can push your ranking down. Keep your website responsive, provide clear headings, and ensure pages load fast. All these elements signal that you value your audience, which can encourage search engines to rank your content higher.
How Do Search Engines Determine Ranking? (People Also Ask)
Search engines examine elements like keyword usage, page load speed, mobile compatibility, site architecture, and off-page signals such as backlinks and social shares. They also measure user interaction, which helps them gauge how satisfying and relevant your page is to a user’s query. According to SEMrush’s Ranking Factors study, factors like direct website visits, time on site, and pages per session all correlate with higher rankings.
The Role of User Experience (UX)
UX covers everything from site layout to how quickly your pages load. A visually appealing website that’s easy to navigate can significantly improve user satisfaction. Google’s Web.dev initiative provides specific metrics to measure UX quality, including Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) and First Input Delay (FID).
When search engines notice positive user signals—fewer bounces, longer browsing times—they tend to reward that site with better rankings. This makes UX a core element of any comprehensive SEO strategy aimed at landing top positions.
Common Ranking Factors and Best Practices
Key ranking factors include quality content, reputable backlinks, optimized on-page elements (like meta titles and headings), and fast performance. Consistency in updating content can also help. Ahrefs’ study of 2 million pages found that it takes an average of 2-6 months for a page to rank in the top 10 search results.
The best practice is to balance human-friendly writing with search engine signals. If you keep providing relevant information and follow search guidelines, you’ll build a strong foundation for staying visible online.
Keyword Fundamentals and Their Role in Ranking
Keywords act like a bridge between a person’s needs and your site’s content. When your website includes those specific terms, you’re telling search engines, “Hey, I’m relevant to this query.” Though the concept seems simple, choosing the right keywords can be surprisingly tricky. Moz’s Beginner’s Guide to SEO explains that effective keyword research involves understanding both search volume and intent.
First, you should recognize the types of keywords that fit your goals. Some phrases, like “how to fix a flat tire,” attract an audience seeking information or tutorials, while others might be more product-focused. Matching your keywords to your website’s objectives not only improves your ranking odds but also aligns with what visitors want.
Low hanging fruit keywords are those with lower competition but enough traffic potential to make them worthwhile. They can help you gain quicker wins. Competitive keywords, on the other hand, tend to have higher search volume but require robust strategies and possibly more resources to conquer. SEMrush’s research found that balancing keyword difficulty with search volume is crucial for SEO success. Understanding this balance can help you prioritize your SEO tasks and get the most out of your efforts.
What Are Keywords? (People Also Ask)
Keywords are the terms people type into search engines to find information, services, or products. They reflect user queries and inform search engines about what your page covers, helping them connect prospective visitors to your content’s main themes. WordStream’s guide to keywords explains that they are foundational to all aspects of search marketing.
Why Are Keywords Important for SEO?
Keywords directly influence whether users find your website when they search. If you align your content with the right terms, search engines pick up those signals and display your pages to relevant audiences. HubSpot’s research shows that properly implemented keywords boost not just traffic, but also engagement and conversions.
Low Hanging Fruit vs. Competitive Keywords
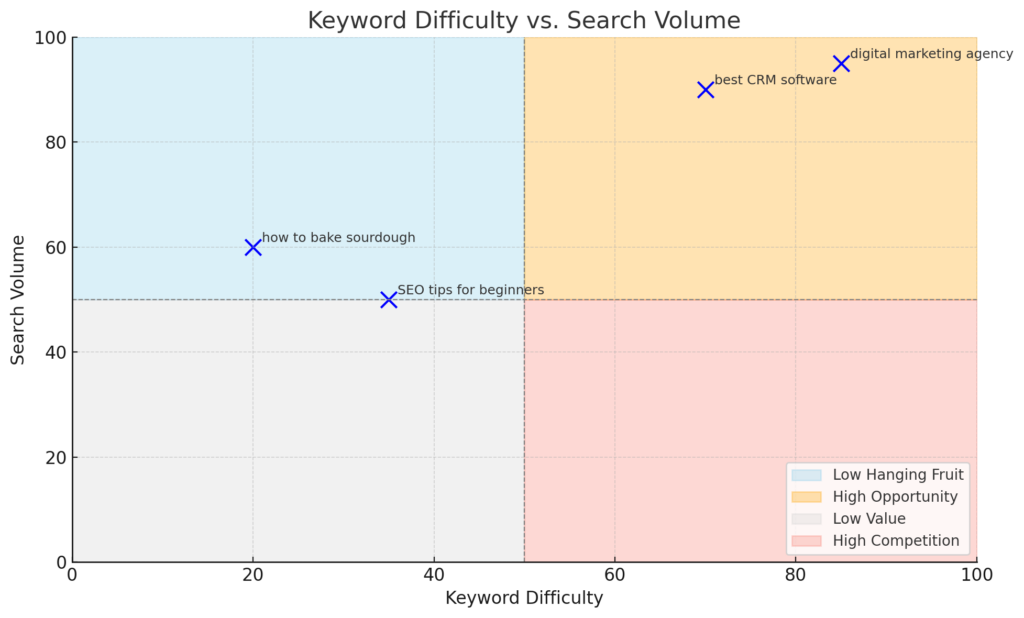
Low hanging fruit keywords often come with moderate search volume yet reduced competition. They let you attract visitors more quickly. An example could be a specific long-tail keyword that targets a niche audience looking for specialized information. Ahrefs’ guide to long-tail keywords explains why these terms often convert better despite lower search volumes.
Competitive keywords bring higher traffic potential but can be harder to rank for, requiring a stronger backlink profile and advanced strategies. According to Neil Patel, it’s often better for newer sites to target less competitive keywords initially while building authority to eventually compete for more valuable terms.
Keyword Research Essentials
Keyword research is about pinpointing which phrases your target audience uses when searching. You might start by brainstorming a few topics, then expand with tools to find variations and search frequencies. This step helps you tap into terms like “how to use Ahrefs for keyword research” or “keyword research for beginners,” ensuring you cover evolving interests. Moz’s keyword research guide outlines a process that starts with business goals and ends with actionable keyword targets.
In recent years, keyword research has expanded to include voice search and user intent. Instead of just focusing on exact-match keywords, many marketers consider question-based queries, such as “What is keyword SEO?” or “How do you do keyword research?” Backlinko’s voice search study found that 41% of voice search results came from featured snippets. By integrating these naturally, you’ll stand out to a broader user group.
When conducting initial keyword research, it’s helpful to look at search volume, competition, and user intent. Give priority to phrases that reflect your audience’s problems and how you solve them. For instance, a café might rank well for local coffee-related terms but also attract widespread traffic through blog posts about unique brewing methods. SEMrush’s guide to keyword prioritization suggests focusing on terms with the right balance of traffic potential and attainability.
How to Do Keyword Research (People Also Ask)

Identify your niche topics, utilize a research tool (like Google Keyword Planner or Ahrefs), then evaluate metrics like search volume and keyword difficulty. Aim for phrases that match your content and have enough potential traffic to justify your SEO efforts. Search Engine Journal’s step-by-step guide provides a comprehensive approach to finding the right keywords.
Keyword Research 2023 and Beyond
From 2020 onward, searches have become more conversational. Voice assistants, such as Siri or Google Assistant, influence how queries are structured. Phrases are longer and more question-based. A recent study by SEMrush found that 20% of all mobile searches are now voice searches.
Focus on thematic clusters of keywords rather than single terms. This approach covers multiple angles of a search, enhancing visibility in both traditional and voice-based results. HubSpot’s topic cluster methodology recommends organizing content around pillar topics and related subtopics.
How to Use Ahrefs for Keyword Research (People Also Ask)
Ahrefs allows you to type in a seed term like “keyword research” to view its volume, difficulty, and related phrases. You can also reveal top-performing content for those keywords to inspire your own content strategy or find link-building opportunities. Ahrefs’ own tutorial provides detailed instructions on how to leverage their platform for comprehensive keyword analysis.
How Keyword Research Has Evolved
In earlier years, many relied heavily on basic keyword matching and volume metrics. Now, we weigh user intent, voice commands, and semantic relationships. The shift encourages a holistic approach—covering multiple keywords in well-structured, user-focused content rather than repetitive, single-term stuffing. Search Engine Land’s evolution of keyword research shows how SERPs have changed to focus more on user intent than exact keyword matches.
Types of Keywords and Strategies
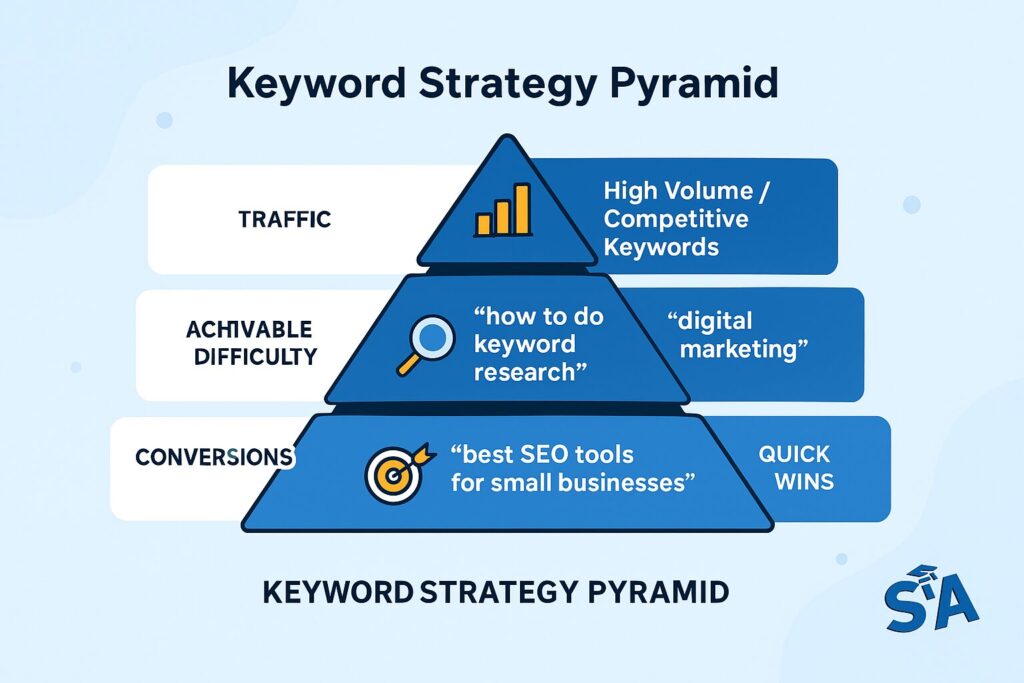
Keywords come in all shapes and sizes. High volume keywords like “digital marketing” or “SEO tips” drive big traffic, but they can be tough to rank for. If you’re just starting out, these might feel like an uphill climb since established competitors often dominate the first pages. SparkToro’s analysis of Google CTR shows that the top three results get over 50% of all clicks.
Achievable difficulty keywords, which have moderate competition, can be a sweet spot for quick wins. These are the terms that many small business owners target first to establish a presence. Focus your content on such phrases, and you might secure stable rankings sooner. Think “how to do a keyword search” or “beginners guide to SEO,” which still have reasonable search volume but a more approachable level of competition.
On the commercial side, certain phrases indicate a buyer on the hunt, like “best SEO tools for small businesses.” By optimizing for these, you can attract visitors who are more likely to make a purchase or sign up for a service. CXL’s buyer intent research found that aligning content with purchase intent can significantly improve conversion rates. Meanwhile, competitive keywords such as “SEO services” or “digital marketing agency” might demand advanced strategies and a quality backlink profile to crack the top positions.
Practical Examples & Tools
When it comes to real-world tactics, let’s imagine a small bakery trying to rank for local keywords. They might examine generic phrases like “bakery in Chicago.” However, for broader content marketing, they can explore “how to bake sourdough at home” or “artisan pastry tips,” which appeals to a national or even international crowd. This approach helps them build authority and brand recognition. BrightLocal’s local search study found that 93% of consumers used the internet to find local businesses in 2020.
Google Keyword Planner is a valuable free tool to kick-start your research. You can type in a seed phrase and see estimated search volume. Another popular option is Google Trends, which highlights seasonality and emerging interests. Combining the insights from these tools gives you a clearer view of which keywords resonate with your target audience.
For deeper analysis, Ahrefs or SEMrush can help you identify keyword difficulty, backlink profiles, and competitor strategies. If you’re focusing on local businesses, keep an eye out for location-based terms such as “[service] in [your city].” Moz’s Local SEO guide shows that proximity is the number one ranking factor for local searches. This ensures you target both generic and location-specific queries, drawing in people who are ready to visit or call. By balancing generic, high-volume keywords with niche terms, you can build steady traffic while also capturing local leads.
Local Keyword Analysis: Generic Scenarios
When running a local site, integrate local phrases like “Chicago café” or “New York hair salon.” Adding “near me” terms into page titles or headings can further boost local visibility. BrightLocal reports that “near me” searches grew by more than 900% over two years. Don’t ignore general keywords either; striking a balance between local and broad terms expands your potential audience.
Google Keyword Research and Analysis
Google’s Keyword Planner and Search Console are a solid starting point for understanding what your audience types into search bars. Search Engine Journal’s guide explains how to extract and analyze Search Console data. Observing metrics like impression counts and average position helps you refine your approach, evolving your initial keyword research into a powerful long-term strategy.
Keyword Searching with Google Ads
Google Ads (formerly AdWords) lets you test keywords by running paid campaigns. You’ll discover which phrases convert best, enabling you to optimize your organic content. WordStream’s PPC and SEO guide shows how paid search data can inform organic strategy. This data-driven approach can amplify your results quickly, though it does require an advertising budget.
Common Questions About Keywords
Readers often ask: “How do you do keyword research?” or “How to do keyword analysis?” These processes revolve around identifying phrases your audience is searching for. Start broad, then narrow it down by reviewing search volume, competition, and user intent. Neil Patel’s step-by-step guide provides a framework that works for businesses of all sizes.
Another recurring question is “How to do a keyword search?” Tools like Google Keyword Planner or Ahrefs simplify the process. You plug in seed terms, and the platform suggests related keywords while revealing their potential reach. Deciding which to prioritize depends on factors like relevance, achievable difficulty, and commercial value. Backlinko’s keyword research tutorial outlines a comprehensive process for finding valuable keywords.
Finally, “What is keyword SEO?” In simple terms, it’s the practice of tailoring site content to match specific keyword demands. By strategically placing these terms (without overdoing it), search engines can more easily pick up on your content’s topic. The end result is a smoother connection between what people are looking for and what your page offers, improving visibility, satisfaction, and conversions. Search Engine Journal’s SEO glossary provides clear definitions of these and other important search marketing terms.
How Do You Do Keyword Research? (People Also Ask)
Combine brainstorming with analytical tools. Consider your brand’s products, services, or reader interests. Then refine that list using traffic metrics and competitor insights. Always remember to factor in user intent—whether it’s informational, navigational, or commercial—to meet your audience’s exact needs. Moz’s keyword research guide explains how to match keywords to different stages of the buyer’s journey.
How to Do a Keyword Search? (People Also Ask)
Use dedicated tools like Google Keyword Planner or a platform such as Ahrefs. Enter seed terms, filter results based on search volume and difficulty, and choose keywords that align with your content goals. Search Engine Watch’s tool comparison helps you select the right platform for your specific needs.
How to Do Keyword Analysis? (People Also Ask)
Keyword analysis involves checking search volume, competition, and relevance to your site. Monitor how you rank over time, adjusting your content and strategy to target promising terms more effectively. SEMrush’s guide to keyword analysis shows how to interpret key metrics like keyword difficulty and click potential.
What Is Keyword SEO? (People Also Ask)
Keyword SEO is the art of optimizing your site around specific phrases that users frequently search for. It covers everything from incorporating these phrases into page titles and headings, to building relevant backlinks and enhancing user experience to improve ranking potential. Search Engine Journal’s guide explains how keywords form the foundation of all SEO activities.
Best Practices for Optimising Your Website
When it comes to on-page SEO techniques, place your target keywords in the page title, meta description, and headings. Keep paragraphs short and ensure the text flows naturally. Yoast’s on-page SEO guide recommends avoiding robotic language as it appeals more to readers, which also makes search engines view your site more favorably.
Off-page SEO techniques revolve around link-building, social media engagement, and community involvement. If you regularly publish helpful content, it’s easier to attract quality backlinks. According to Backlinko’s analysis of 11.8 million Google search results, the number of referring domains correlates strongly with higher rankings. Equally important, keep an eye on brand mentions or user reviews. Demonstrating authority and trustworthiness can lift your site’s ranking in the long run.
One of the biggest pitfalls is keyword stuffing, which happens when you cram your page with repeated terms. Instead, focus on providing authentic, relevant information. Google’s own guidelines warn against this practice and encourage focusing on users first. Monitor changes in your results, and update your strategy accordingly. SEO isn’t a one-time fix; it’s an ongoing process of fine-tuning and learning from shifts in user behavior.
On-Page and Off-Page SEO Techniques

On-page SEO focuses on structured content and keyword placement. Off-page involves building your site’s authority through endorsements (links) and social signals. Moz’s guide to both on-page and off-page SEO explains why both are essential to ranking well in search engines.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls Like Keyword Stuffing
Overusing the same term can lead to penalties and a poor user experience. Search Engine Journal’s article on keyword stuffing shows examples of what to avoid. Keep your keyword usage natural and varied, ensuring every mention offers genuine value to readers.
Monitoring and Adjusting Your SEO Strategy
Tools like Google Search Console, Google Analytics, and Ahrefs give you insights into how your SEO efforts perform. Track traffic, keyword positions, and user engagement. Search Engine Watch’s guide to SEO KPIs explains which metrics matter most. Based on the data, revise your approach to capitalize on successes and address any weaknesses.
Summing up, search engines work by crawling websites, gathering data, and indexing pages so they can quickly retrieve that information whenever a user types in a query. Ranking then determines the order in which webpages appear, and those that combine relevance with authority float to the top. Whether you’re a local café aiming to attract nearby visitors, or an e-commerce store seeking global reach, understanding this process is your ticket to improved visibility.
Equally crucial to your success is thorough keyword research. By identifying the right phrases—ranging from low hanging fruit keywords to more competitive ones—you can tailor your content and stand out among the crowd. Tools like Google Keyword Planner and Ahrefs help you pinpoint opportunities, while consistent monitoring ensures you keep evolving your strategy.
Ultimately, making the most of these search engine fundamentals won’t just amplify traffic to your site. It will also cultivate a smoother user experience and build genuine trust with your audience. As you refine your SEO techniques, remember that what truly matters is helping people find what they need. If you do that well, search engines will reward you with the spotlight you deserve.

